Today, the disease of arthrosis of the joints has become the most common among all pathologies of the musculoskeletal system. In addition, urban dwellers, people who are accustomed to leading a sedentary lifestyle and those who have recently suffered injuries of varying degrees of intensity, most often suffer from joint disorders.
The forecasts of doctors in this regard are disappointing. It is assumed that in the near future the number of people suffering from various forms of osteoarthritis of the large joints will only grow. According to the latest data, about 7% have experienced all the symptoms and consequences of osteoarthritis.
This disease has become a major cause of disability and reduced performance. It is characteristic that the peak of incidence occurs in the age groups from 40 to 60 years, and not only in elderly retirees, as is mistakenly believed.
What is osteoarthritis?
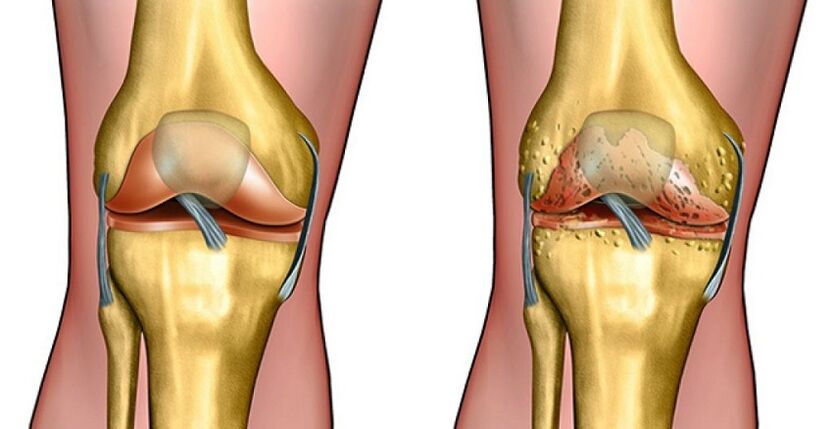
Osteoarthritis (another name for osteoarthritis) should be understood as a complex degenerative pathology in which the cartilage plate of the bone that forms the joint is destroyed. The reasons lie not only in the processes occurring in hyaline cartilage.
There are many other prerequisites for the disease.
Arthrosis of the joints develops under the condition:
- excessive physical activity. Usually, overweight people get sick in these cases. Human joints are not designed for constant movement with a high load. For this reason, the increased compression suffered by the knees during activity becomes a prerequisite for micro-trauma to the cartilage tissue. There is a violation of the sliding properties of tissues and a decrease in joint mobility. Athletes often suffer that they have systematically damaged the joints due to abrupt and frequent changes in natural pressure between the joint surfaces or from high loads with insufficiently heated joints;
- congenital or acquired deformities, lesions of the musculoskeletal system. In such conditions, the disease is provoked by inadequate contact of the articular surfaces of the bone. Absolutely the entire load is unable to be distributed over the joint, and injuries are formed in places of excessive compression. A striking example of such a violation will be rickets, scoliosis and kyphosis. It should also include improper fusion of broken bones, various deformities of the limbs;
- violation of cartilage regeneration. This mechanism of development of arthrosis is observed in the presence of an inflammatory process in the body, impaired blood circulation and hormonal disorders. The problem is based on inadequate restoration of lost cartilage tissue, lack of natural remodeling and thinning;
- problems with the formation and production of synovial fluid. In case of insufficient joint fluid, the rubbing surfaces are constantly injured, their wear and inflammation accelerates, the general condition of the body worsens.
Stages of arthrosis
Since osteoarthritis of the disease causes the destruction of the cartilage tissue of the joint, its symptoms vary significantly depending on the stage of the pathological process.
As a result of the active destruction of the joint surface, a person will experience new symptoms, and the prognosis for the restoration of motor activity will not change. Based on the clinical picture of the disease, the doctor will choose the optimal method of treatment and drugs.
1st degree arthrosis is characterized by the fact that discomfort and slight pain are felt only after intense and prolonged exertion. After a short rest, the signs that arose during physical activity disappear.
In this case, the joint injuries will not be visible on the X-ray photo, but a slight narrowing of the joint space is possible.
Stage 2 of the pathology is characterized by an increase in symptoms. Now there are pains not only due to prolonged activity, but also with small movements of the limbs.
Rest will not bring the desired relief. There is stiffness in the movements, the mobility of the joint is limited. At this time it is recommended to reduce the load on the affected joints, but it should not be completely excluded, otherwise muscle atrophy occurs. An x-ray will show clear signs of osteoarthritis:
- bone growth;
- deformation;
- neoplasms (osteophytes) near the joint space, its narrowing.
When the disease reaches its final stage, joint injuries cause constant, excruciating pain. Therefore, at the reflex level, a person begins to sharply limit his movements, to protect the affected joint from stress. Pain syndrome also occurs during sleep and rest, when the joints are at rest.
The patient is forced to take the position in which it hurts less. Movement becomes possible only with the help of a wheelchair or crutches.
It is characteristic that the 3rd and 4th degrees of osteoarthritis can completely deprive a person of the ability to walk due to fusion of the joint surfaces (ankylosis).
Which joint is most often affected?
According to medical statistics, the lower limbs are more susceptible to osteoarthritis. Joints suffer from inflammation and degeneration: hip, knee.
If you have hip joint problems, pelvic pain is initially felt after a long walk or run. With active progression of the pathology, pain intensifies and mobility is limited.
A person will notice unpleasant stiffness in the joint, and in certain positions the stiffness increases several times at once. In the last stages of arthrosis of the hip joint, the patient unconsciously protects the affected leg and tries not to step on it at all. He doesn't move his pelvis, which helps relieve the pain.
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint is manifested by discomfort and aching pain after walking. There are no external manifestations of the problem and inflammation. The most common prerequisite for osteoarthritis of the knee joint is its past trauma against the background of damage to internal structures.
Such injuries, as a rule, cause abnormalities in the adjacency of the contact joint surfaces. It also takes place:
- overload some areas of the cartilage;
- their rapid wear.
The changes, as in the previous case, depend on the degree of arthrosis. You should also take into account the causes of the disease, the availability of adequate medical care, the general condition of the body and the dynamics of the pathological process. Some forms of the disease do not make themselves felt for a long time and do not progress.
Sometimes, even for decades, there is no noticeable deterioration of the knee. In other cases, there is a rapid increase in symptoms and a high likelihood of loss of mobility.
Get rid of arthrosis
Today there are 2 main directions in the treatment of arthrosis of the large joints: medical and surgical.
First of all, the treatment is aimed at rapidly improving blood circulation in the diseased joint and accelerating the properties of cartilage tissue with the help of drugs. Anesthesia and removal of inflammation are also needed. For this purpose, doctors practice the use of the following drugs.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
These drugs interfere with the natural chemical chain in the cartilage that causes inflammation. There is swelling in the tissues, pain appears, and the strength of the cartilage decreases during movement.
Thanks to the use of anti-inflammatory drugs it is possible to reduce or completely stop the pain syndrome. The initiation of the so-called inflammatory chain process is also prevented, which helps accelerate the regeneration of the affected areas.
Medicines are produced in the form of tablets, powder and rectal suppositories. The tactics of treatment, the choice of a specific drug is determined by the doctor strictly on an individual basis, based on the clinical picture of the disease, its dynamics and concomitant pathologies.
Opioids and chondroprotectors
Powerful centrally acting analgesics are called opioids. Usually, such drugs have a narcotic effect on the body, increasing the thresholds of pain sensitivity. Thanks to this treatment it is possible to reduce pain in the affected joints.
The use of drugs in this group should be strictly under the supervision of the attending physician, as such drugs cause mental and physical addiction.
To accelerate the restoration of cartilage tissue, special means are used - chondroprotectors. In general, it is the structural elements of the cartilage itself, which allows them to have an activating effect on their recovery.
These medicines include:
- chondroitin sulfate;
- glucosamine sulfate;
- hyaluronic acid.
Chondroitin and glucosamine are organic substances abundant in the intercellular space of the cartilage. The mechanism of their action on the joints is not yet fully understood, however, it has been repeatedly shown to have a positive effect on the regeneration of cartilage tissue during treatment.
Chondroitin-based drugs activate the production of special substances from the extracellular matrix of cartilage (proteoglycans and hyaluronic acid). At the same time, the resorption process in the tissues is significantly inhibited. Similarly, some chemical processes are suppressed, there is a decrease in inflammation of the cartilage, damage and severity of the pain syndrome.
Long-term use of drugs in this group is often required. A course of treatment for at least 6 months is required. Otherwise, the benefits of the therapy should not be expected. The organic combination of chondroitin and glucosamine is most commonly practiced. However, clinical studies have not confirmed a significant difference between such treatment and the use of only one of the chondroprotectors.
Despite the obvious benefits and safety, not everyone can treat osteoarthritis of the joints with such drugs due to the relatively high cost.
Hyaluronic acid is no less common in modern medicine. It is a long chain of carbohydrates that provides elasticity and viscosity to the synovial fluid. The unique properties of hyaluron are largely responsible for the good flow properties of the joint fluid.
Intra-articular injections of the drug have a good effect on the state of the body, because studies have shown that osteoarthritis is often triggered by a decrease in the concentration of hyaluron within the joint and a shortening of the chain of its molecules.